Analysis of Appliance Energy Efficiency Ratings and Lighting Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency ratings are power consumption parameters for appliances, determined according to EU directives. They provide a direct reflection of a product's energy efficiency and affordability, helping consumers quickly identify appliances that meet their needs when purchasing.
The energy efficiency of artificial lighting is influenced by multiple factors, including the performance characteristics of the lighting fixture itself and the properties of the illuminated object. Specifically for indoor lighting scenarios:
From an environmental and spatial perspective, energy efficiency depends on the utilization of natural light, the overall interior design, and the color and texture of walls, ceilings, and furniture. Cleanliness also has an impact.
From the perspective of lighting fixtures themselves, energy efficiency is constrained by core components such as the fixture's internal power supply and optical system. The energy efficiency of the light source used is a key factor in determining overall lighting energy consumption.
The Evolution of Energy Efficiency Labeling
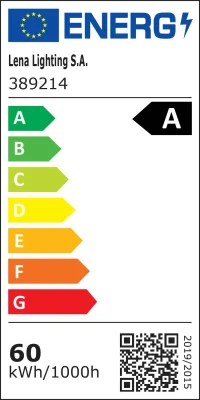
The EU issued its first energy labeling directive, 92/75/EC, in 1992, and has promoted its implementation through targeted product application directives. The directive established the first energy labeling system, using a seven-level alphabetical rating and corresponding color coding to identify appliance energy efficiency: Grade A (green) represents the most energy-efficient products, while Grade G (red) represents the least efficient. This simple and intuitive grading system allows consumers to quickly compare the energy efficiency levels of different products without having to analyze complex product parameters. The labels also include additional market reference information.
In 1998, the EU further issued a specific energy labeling directive for household lighting—Directive 98/11/EC. However, the labeling system specified in this directive applies only to household lighting and excludes certain types of reflector lamps and low-voltage lamps.
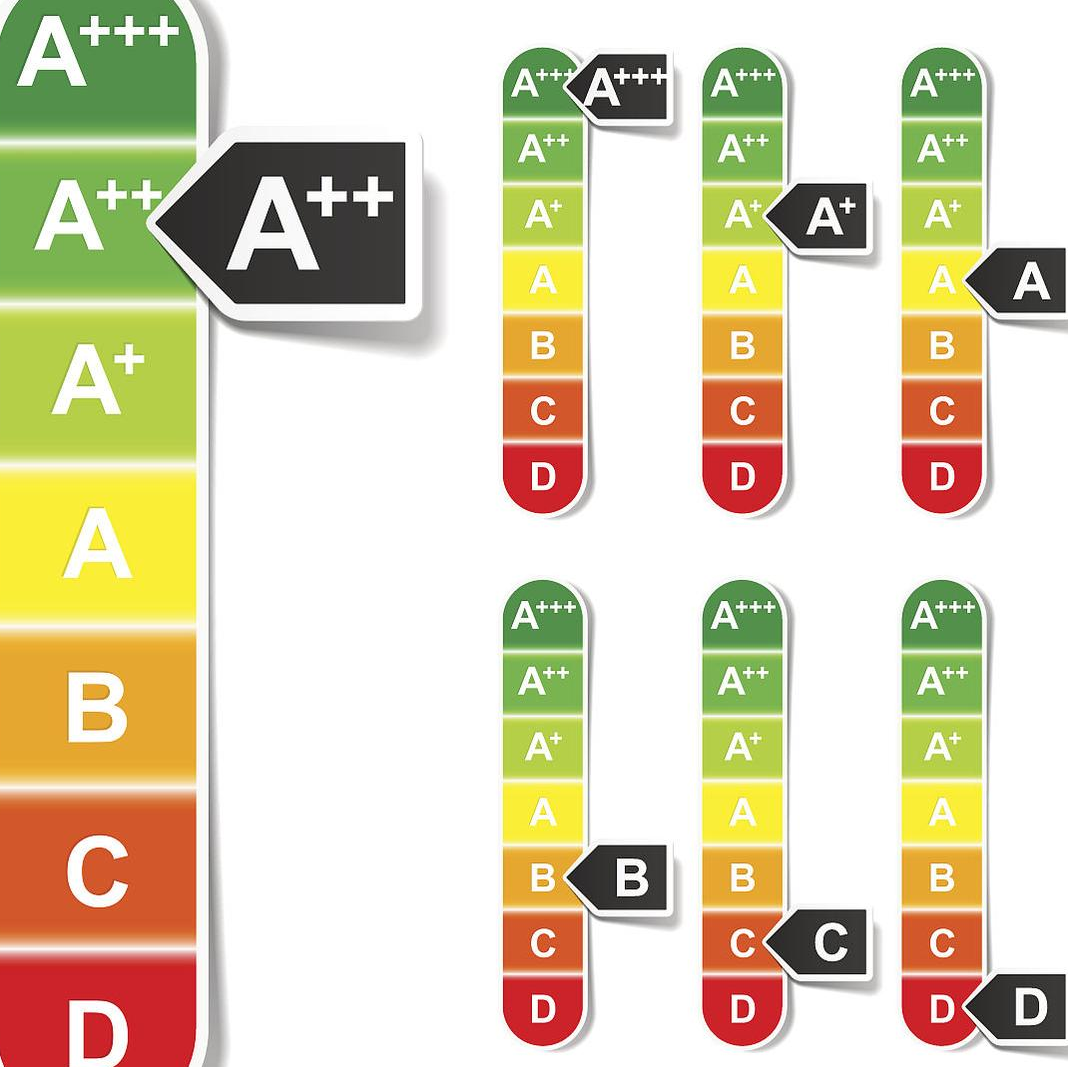
With technological advances since 1992, the energy efficiency of all types of electrical appliances has generally improved. To adapt to this change, the EU introduced a new directive 2010/30/EU, which officially replaced the original directive 92/75/EC. On the basis of the original classification, it added three higher energy efficiency grades: A+, A++, and A+++, further refined the energy efficiency evaluation standards, and more accurately reflected the energy-saving level of current electrical products.

