LED technology is a technology that utilizes light-emitting diodes (LEDs). LED technology is designed to illuminate spaces more efficiently. LED lighting far surpasses traditional lighting in terms of energy efficiency.
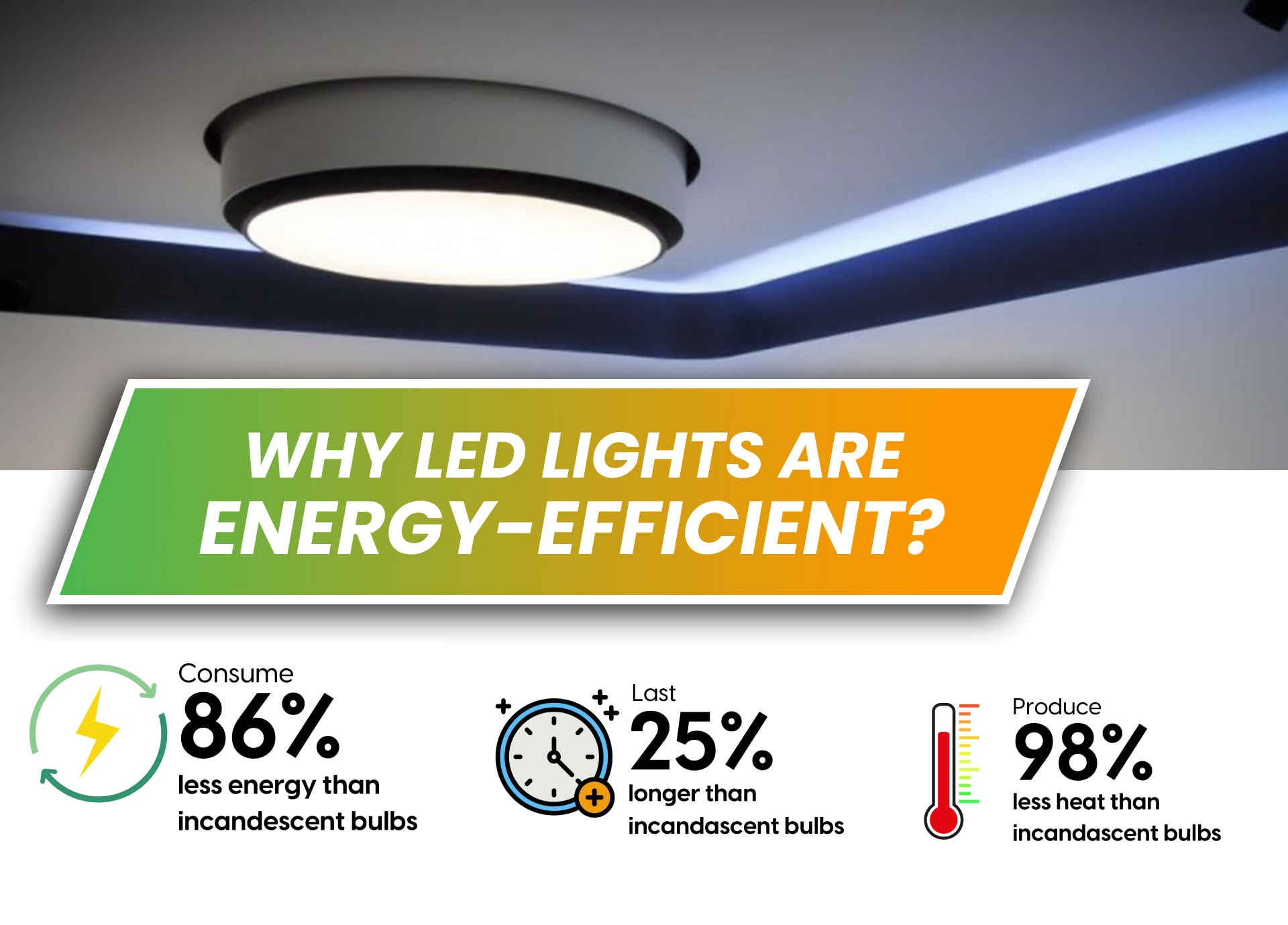
Here are some reasons to support this claim. Here are four reasons why LED lights are more energy-efficient than traditional lighting:
✅ Directional lighting efficiency – LEDs emit light in a specific direction, reducing energy waste from scattered light and the need for reflectors or diffusers, which are common in traditional lighting solutions.
✅ Lower energy consumption – LEDs use up to 80% less electricity than incandescent bulbs and approximately 50% less electricity than CFLs, enabling them to efficiently convert energy into light rather than heat.
✅ Longer lifespan – Compared to traditional bulbs, LED bulbs have a significantly longer lifespan (up to 50,000 hours or more), reducing the need for frequent replacement and further saving energy in manufacturing and shipping.
✅ Minimum Heat Emissions – Unlike incandescent bulbs, which waste a significant amount of energy as heat, LEDs generate very little heat, ensuring that more energy is used for lighting rather than lost as heat.
Unique Features of LED Lights
LEDs are semiconductor devices that produce light when an electric current flows through them. Characteristics of LED lights include:
They use less energy to produce light
Generate less heat
The light is composed of different colors, which change color when a switch is flipped.
LED lights contain a diode that converts electrical energy directly into light, making them more efficient and durable.
As mentioned above, a diode is an electronic component with two electrodes (anode and cathode). Current flows through these electrodes, flowing from the anode to the cathode. Silicon is one of the materials used to make diodes.
Incandescent bulbs, on the other hand, produce light by heating a filament.
The filament glows when heated to a certain temperature. In a filament bulb, the metal filament is surrounded by a translucent glass bulb filled with an inert gas or vacuum.

Energy Efficiency
The energy efficiency of an LED light is a key consideration.
These metrics include watts and lumens. Light is measured in lumens, while the electrical power generated by a device is called wattage.
Incandescent and CFL bulbs use more wattage than LED bulbs. A 7-10 watt LED bulb produces the same amount of light as a 60-watt incandescent and a 15-watt CFL bulb. They both have a luminous flux of 650-850 lumens. LEDs use 80% less energy than traditional bulbs.
The amount of light produced per watt of electricity consumed is measured in lumens per watt (lm/W). LED bulbs can produce significant brightness with only a few watts. When purchasing LED bulbs, be sure to check lumens per watt.
For example, LEDs (100-150 lm/W) outperform incandescent bulbs (10-17 lm/W).
LED lights are no longer a necessity, but a lifestyle requirement because of their energy efficiency, longevity, and flexibility.
The lifespan of an LED bulb is approximately 25,000 hours. LEDs are highly sought after due to their energy efficiency, which reaches up to 80%.
Why LEDs are more energy-efficient
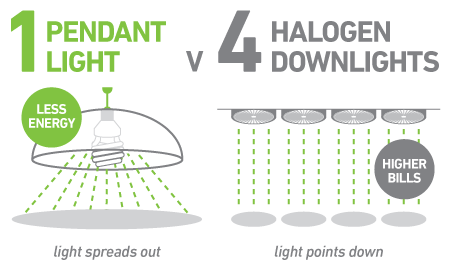
Energy Consumption Comparison of LED Pendant Lights and Halogen Lamps
First, it's important to note that efficiency is measured by the amount of energy consumed. Compared to traditional incandescent bulbs, LEDs consume less energy for the following reasons:
✅ Traditional incandescent bulbs use a filament to generate light. A large amount of current heats the filament. The filament only emits light when current flows through it, and it remains hot until it emits photons. Therefore, it consumes more energy.
On the other hand, LEDs produce light when current flows through the material, causing positive and negative charges to combine. This process is called electroluminescence. In LEDs, most of the energy is used to generate light, rather than generating both light and heat.
✅ LEDs emit light in only one direction, avoiding energy loss in unnecessary directions. In contrast, incandescent light diffuses, causing energy to be lost in unimportant directions. Ultimately, incandescent bulbs consume more energy.
Longevity and Durability
Lifespan refers to the expected lifespan of a bulb. Incandescent bulbs generally have the shortest lifespan. Durability, on the other hand, refers to a bulb's ability to withstand damage or stress. LED bulbs excel in durability.
This is because they are less susceptible to damage, thus reducing waste.
The average lifespan of an LED bulb is 50,000 hours. LED bulbs come in a variety of shapes, housings, and styles, and are designed to last a long time.
When the luminous flux of an LED bulb decreases, the bulb becomes dimmer. The lifespan of a bulb is measured when the luminous flux drops below 70% or 50%. Once the luminous flux falls below 70% or 50% of its original output, the bulb is dead.
In comparison, incandescent bulbs have a lifespan of approximately 1,000 hours and are also less durable.
Lastly, CFL bulbs have a lifespan of 8,000 to 20,000 hours. Replacing them takes a long time, making them second only to LED bulbs in durability. The lower replacement requirements make them more energy-efficient.

