In modern times, incandescent light bulbs remain popular due to their affordability and ease of use.
Thomas Edison's Contributions to the Light Bulb
Thomas Edison's most famous achievement was inventing the practical incandescent light bulb. He also founded the Edison Electric Light Company. In 1882, he introduced direct current (DC) to Manhattan, marking a significant milestone.
Light Bulb
When he added a carbon filament, the incandescent light bulb finally reached a practical stage. These inventions made the bulb more durable and an affordable option for everyday use.
After inventing the light bulb, Edison dedicated himself to developing the entire electrical system. He established all the components needed for large-scale power transmission and developed generator, distribution network, and meter technology.
In 1882, the Pearl Street Power Station brought electricity to residential and commercial users.
Through commercial operation, Edison sparked a revolutionary change in lighting technology. This invention replaced gas lamps and laid the foundation for the modern electrical system.
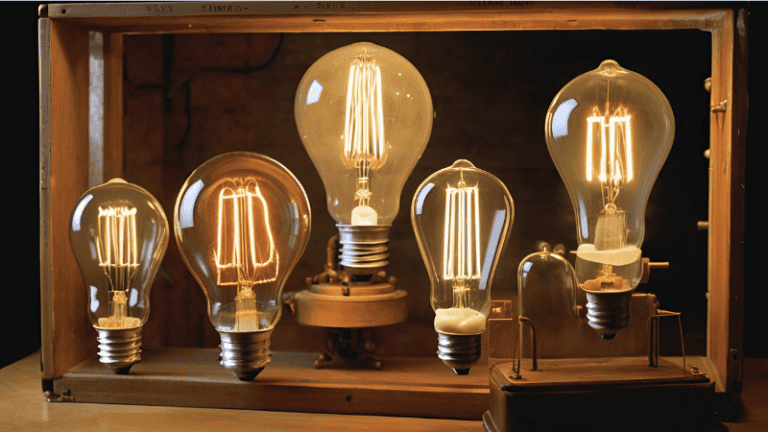

Nikola Tesla and His Role in Electrical Innovation
Nikola Tesla's pioneering technology changed the way we use electricity. He laid the foundation for modern electrical systems.
Tesla's Innovations
Tesla developed and popularized alternating current (AC), enabling the transmission of electricity over long distances. This made power generation and transmission more convenient and economical worldwide.
His research into high-frequency electricity propelled the development of fluorescent and neon lights. While Tesla was not the inventor of the light bulb, his work advanced lighting systems. He demonstrated early versions of fluorescent and neon lights at the 1893 Chicago World's Fair.

Tesla also invented the Tesla coil, crucial for wireless power experiments. It played a significant role in high-voltage physics, radio technology, and neon lighting.
He played a key role in the construction of the Niagara Falls hydroelectric power station. This project was a major step towards large-scale power supply using renewable energy.
Tesla's ideas about multiphase systems and induction motors revolutionized how industry used electricity. These innovations made electricity more readily available to homes and factories.
His vision continues to inspire technological advancements today. His work laid the foundation for wireless communication, radio, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth.
Tesla's Light Bulb
Patent Wars: Edison vs. Tesla
In the 19th century, Edison and Tesla engaged in a fierce debate over direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC). After Tesla introduced his electrical system, Edison spread misinformation about its safety. He warned the public that this system would pose serious health risks and could lead to fatal accidents.
Edison reinforced his argument by using AC to shock animals. He used these gimmicks to demonstrate the dangers of the technology. He also funded the construction of the first electric chair using AC. This associated the technology with danger and death.
In public demonstrations, Tesla proved the safety and efficiency of his AC system by allowing current to flow through his own body. This helped people trust the new technology.
Soon afterward, AC became the preferred method for future electricity transmission. The successful operation of the Niagara Falls hydroelectric power station confirmed the value of AC. It demonstrated that AC was the best choice for long-distance power transmission.
Edison vs. Tesla
The innovation of the AC power system made long-distance power transmission possible. Edison initially overlooked Tesla's revolutionary ideas, later admitting his mistake. Tesla's work laid the foundation for the electrical systems we use around the world today.
Both Edison and Tesla were brilliant inventors, but their motivations were drastically different. Edison focused on commercial success, building profitable systems such as the incandescent light bulb and power distribution networks.
In contrast, Tesla was driven by visionary ideas. His work on alternating current, wireless power, and the Tesla coil aimed to transform the way the world uses electricity.
| Point of Comparison | Nikola Tesla | Thomas Edison |
|---|---|---|
| Electricity Type | Alternating Current (AC) | Direct Current (DC) |
| Approach | Scientific and visionary | Practical and business-oriented |
| Key Inventions | AC motor, Tesla coil, wireless tech | Light bulb, phonograph, motion pictures |
| Innovation Style | Theoretical, ahead of his time | Hands-on, focused on profit |
| View on Energy | Wanted free energy for all | Capitalized on inventions |
| Public Recognition | Gained fame after death | Famous and wealthy in his lifetime |
| Legacy | AC became the global standard | DC is used in limited applications today |
The Tesla Light Bulb Myth: Distinguishing Fact from Fiction
Many people associate Nikola Tesla with the invention of the light bulb because of his contributions to the field of electricity. However, the light bulb was not Tesla's invention; Thomas Edison and earlier inventors deserve more credit. Tesla's contributions to radio and high-frequency electricity propelled the development of the discharge lamp.

His research into artificial sunlight and electrical systems had a profound impact on modern lighting technology. Although he was not the inventor of the light bulb, his reputation as an inventor has led many to associate him with it.
The public often attributes scientific progress to Tesla, overlooking the importance of collaboration. His work on electrical systems and wireless power was crucial to the development of lighting and other technologies.
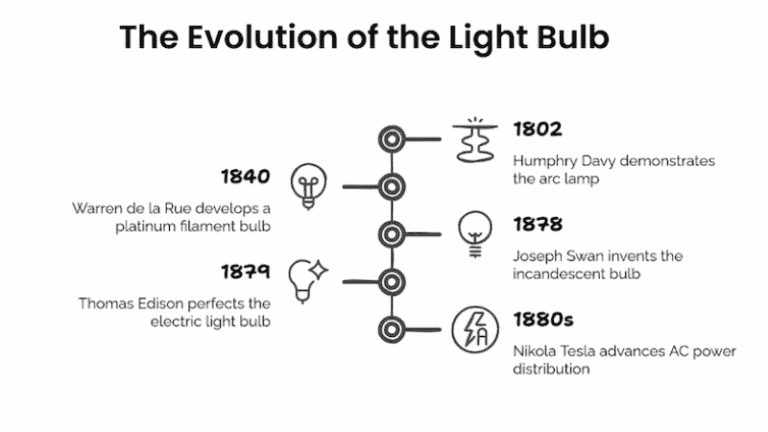
The Evolution of the Light Bulb: From Edison's Incandescent Bulb to LED Lights
Thomas Edison invented the practical incandescent light bulb, which used a carbon filament in a vacuum pump. This design made lighting affordable and reliable.
Halogen Bulbs
Fluorescent bulbs subsequently appeared, using electricity to excite mercury vapor. The mercury vapor produced ultraviolet light, which was converted into visible light by a phosphor coating.
Halogen bulbs improved upon incandescent bulb technology. They used an inflatable chamber, resulting in a longer lifespan and higher brightness. LED technology developed in the 1960s and has continued to improve over time. LED lights are widely popular due to their energy efficiency and long lifespan.
Today, LED lights dominate the market in both residential and industrial sectors. This shift demonstrates society's strong push for efficient and sustainable lighting.

